Nvidia GeForce RTX 4060 Ti (8GB) review: Disappointing for $400

 Image: Brad Chacos/IDG
Image: Brad Chacos/IDGAt a glance
Expert’s Rating
Pros
Fast 1080p gaming for high refresh rate monitorsKiller Nvidia features: DLSS 3, Reflex, RTX Video Super Resolution, Broadcast, and moreTremendously power efficientAV1 encodingSame price as RTX 3060 Ti
Cons
8GB of memoryGPU and memory bus changes make it unappealing for 1440p gaming; may need to reduce settings in some 1080p Ultra gamesDLSS negatively affects image quality at 1080p resolutionSingle-digit, essentially stagnant raw performance upgrade vs. 3060 TiMust use ugly 8-pin to 12VHPWR adapter (included)$400 is a ton of money for a 1080p GPU
Our Verdict
The GeForce RTX 4060 Ti 8GB brings Nvidia’s awesome DLSS 3 mainstream, but offers disappointing value as an upgrade to the 3060 Ti and as a standalone 1080p gaming option in 2023. Technical decisions also make it unappealing for 1440p gamers, unlike its predecessor.
Price When Reviewed
$399 (8GB)
Best Prices Today: GeForce RTX 4060 Ti (8GB)
RetailerPrice $399View DealPrice comparison from over 24,000 stores worldwideProductPricePrice comparison from Backmarket
$399View DealPrice comparison from over 24,000 stores worldwideProductPricePrice comparison from Backmarket
At first blush, Nvidia’s $399 GeForce RTX 4060 Ti (8GB) looks like it should be a smashing success.
Its predecessor, 2020’s $399 GeForce RTX 3060 Ti, was one of the best GPUs in a strong RTX 30-series generation, offering impeccable 1080p and spectacular 1440p gaming performance at a reasonable price. The new RTX 4060 Ti sticks to the same price while weaving in Nvidia’s latest killer RTX 40-series features, like DLSS 3, Reflex, RTX Video Super Resolution, best-in-class ray tracing, AV1 encoding, stunning power efficiency, and more.
But peel back the hood and things aren’t quite so clear cut.
Nvidia made technical decisions—reducing core counts and altering the memory subsystem—that allow the GeForce RTX 4060 Ti to scream at 1080p resolution but make it unappealing for 1440p gaming. It also makes the 4060 Ti a mediocre generational upgrade in terms of raw firepower. The decision to outfit this card with 8GB of memory means it won’t be able to run all games with eye candy maxed out even at 1080p, by Nvidia’s own admission. And while the addition of DLSS 3’s AI-generated frames is certainly welcome, image upsampling technologies create noticeable visual artifacts at the less pixel-packed 1080p resolution, rendering DLSS’s performance-boosting advantages less of a factor here.
So I guess the bottom line is: Are you willing to pay $400 for a 1080p graphics card with 8GB of memory in the year of our lord 2023?
What are the Nvidia GeForce RTX 4060 Ti’s specs and price?
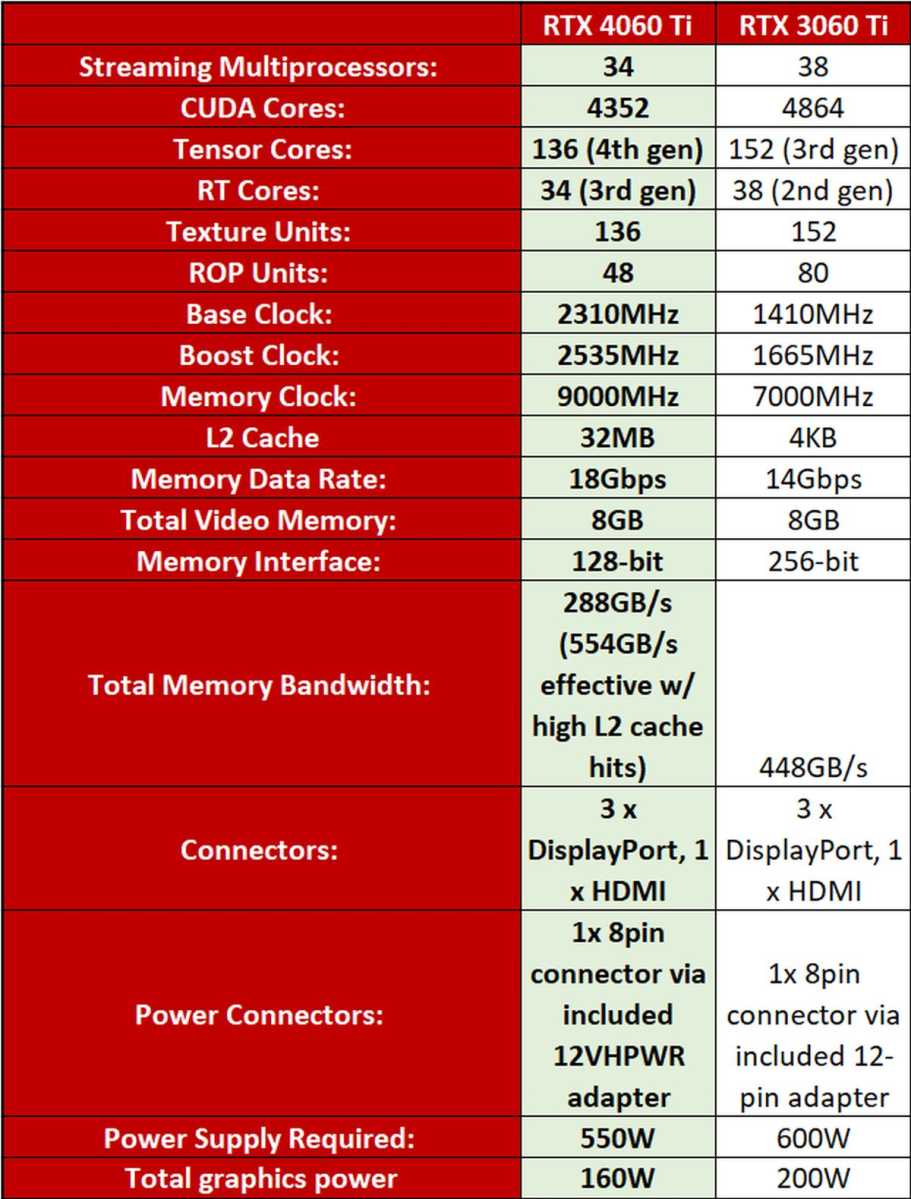
Nvidia revealed some high-level details for the GeForce RTX 4060 Ti 8GB in its announcement (which also revealed a $299 RTX 4060 and $499 RTX 4060 Ti 16GB, both coming in July) but didn’t provide deeper technical information. Here that is, compared against the RTX 3060 Ti:
Brad Chacos/IDG
Brad Chacos/IDG
Brad Chacos/IDG
A few key details leap out straight away. First, the RTX 4060 Ti—built upon Nvidia’s new “Ada Lovelace” GPU architecture—is tremendously power efficient and offers much higher GPU and memory clock speeds than before. Bravo, Nvidia.
Second, this new card actually holds significantly fewer CUDA, tensor, and RT cores than the RTX 3060 Ti it replaces. Because of this, the RTX 4060 Ti can actually be slower than its predecessor in some situations, and only offers a middling performance uplift overall. Best-case scenarios top out at around 15 to 20 percent faster than the RTX 3060 Ti, but you’ll see essentially static gen-on-gen performance in many more games and resolutions. It’s a testament to Lovelace that this GPU shows any speed upgrades considering how many fewer CUDA cores it has, especially given the ultra-low power draw, but it’s still deeply meh as a generational upgrade.

Brad Chacos/IDG
Brad Chacos/IDG
Brad Chacos/IDG
Third, Nvidia adjusted the GeForce RTX 4060 Ti’s memory subsystem to more closely mirror AMD’s Radeon Infinity Cache setup, plopping a big L2 cache on-die while nerfing the memory bus width all the way down to 128 bits. (The 3060 Ti has a 256-bit bus.) Nvidia also kept memory capacity identical to its predecessor at 8GB of GDDR6, in an era when modern games can now eat more than that even at 1080p resolution. And when it comes to VRAM capacity, either you have enough or you don’t.
The memory configuration prevents the GeForce RTX 4060 Ti from being a viable High/Ultra 1440p gaming option in the long-term, and even in many situations now. We explained why in our analysis during the RTX 4060 Ti’s initial reveal:
“The memory bus width is being slimmed down, from 256-bit in the RTX 3060 Ti to just 128-bit in the 4060 Ti. Think of it like traffic congestion; if memory requests are cars, the bus width is the size of the road. A hundred cars move much faster on a four-lane highway than a single lane dirt road, and that speed is analogous to the card’s overall memory bandwidth. Ostensibly, the GeForce RTX 4060 Ti offers 288GB per second of overall memory bandwidth, compared to the 3060 Ti’s 448GB/s—a huge gulf.
It’s not that simple though.
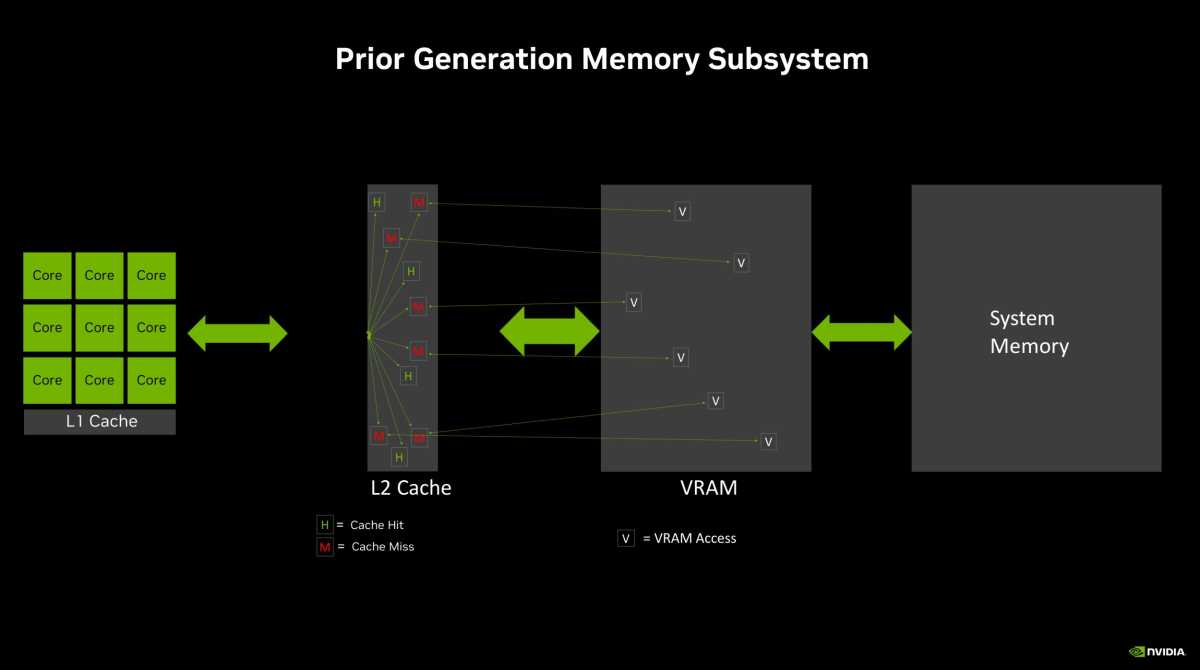
An illustrative example of how traditional GPU memory works, without a larger on-die L2 cache.
An illustrative example of how traditional GPU memory works, without a larger on-die L2 cache.
Nvidia
An illustrative example of how traditional GPU memory works, without a larger on-die L2 cache.
Nvidia
Nvidia
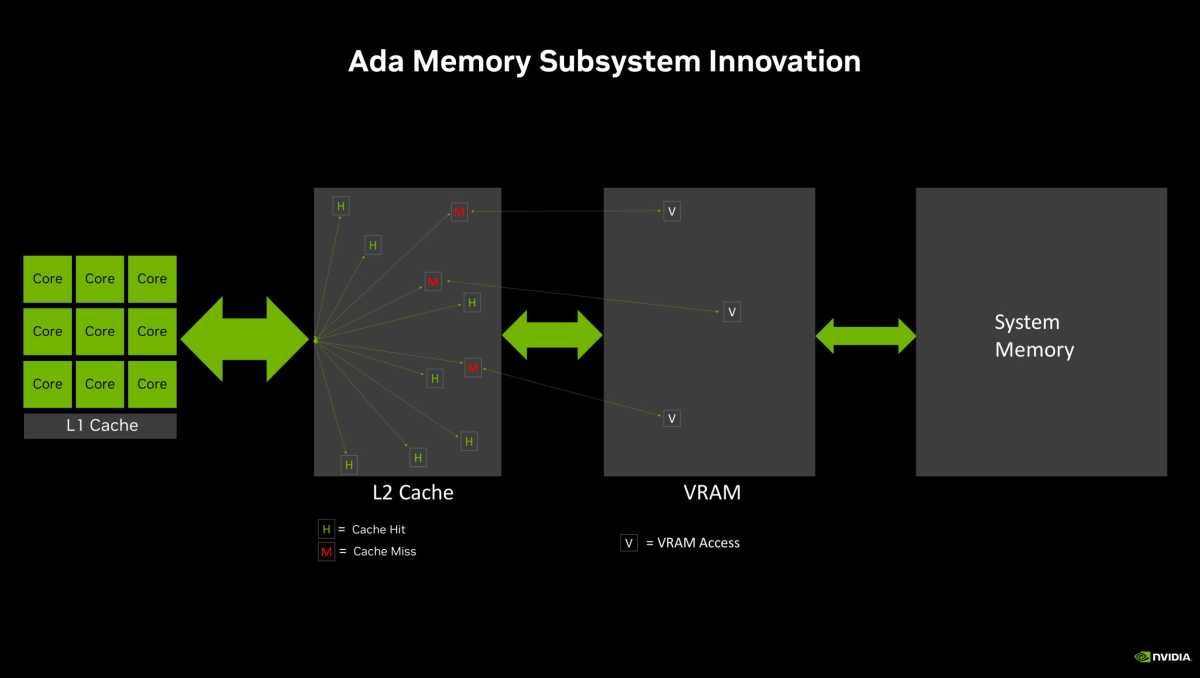
A comparison image showing how the larger L2 cache in Nvidia’s RTX 40-series (“Ada Lovelace”) GPUs helps result in far fewer calls to traditional memory.
A comparison image showing how the larger L2 cache in Nvidia’s RTX 40-series (“Ada Lovelace”) GPUs helps result in far fewer calls to traditional memory.
Nvidia
A comparison image showing how the larger L2 cache in Nvidia’s RTX 40-series (“Ada Lovelace”) GPUs helps result in far fewer calls to traditional memory.
Nvidia
Nvidia
Nvidia swiped a page from AMD’s killer Infinity Cache technology for RTX 40-series offerings, dropping a large on-die cache onto the GPU itself, and the RTX 4060 family is no different. Not only does the closer physical proximity mean this cache is faster, but deploying it also reduces the need to send many requests out to the memory chips arrayed around the GPU itself, as illustrated in the slides above. While AMD’s Infinity Cache uses an L3 cache, Nvidia opted for a 32MB L2 cache instead (versus just 4MB on the 3060 Ti). The company says the larger L2 cache particularly helps improve ray tracing and DLSS performance, and results in the “effective” memory bandwidth shown in the technical specifications slide.
Here’s the thing though: As evidenced in our review of the last-gen Radeon RX 6600 XT, which had 32MB of Infinity Cache and a 128-bit bus, pairing a big on-die cache with a neutered bus width helps the GPU perform exceptionally—both in performance and power—at the display resolution it’s targeted for, but usually results in lower-than-expected results at higher resolutions. Higher resolutions have higher memory needs, which results in fewer successful on-die cache hits. When that happens, the memory requests go out to traditional memory—and the RTX 4060 Ti’s much smaller 128-bit bus might falter when that happens.”
Now that we’ve tested the RTX 4060 Ti, we can confirm that it indeed slows down at the higher 1440p resolution. In fact, it can’t even hang tough at 1440p with the RTX 3070, which cost $500 in 2020. You’d expect a new card to at least rival an older GPU that cost just $100 more than it 2.5 long years ago, but the RTX 4060 Ti fails to clear that low bar.
Nvidia seems to be hitching the 4060 Ti’s star to Lovelace’s power efficiency and the company’s GeForce feature set, which is admittedly killer: DLSS 3, RTX Video Super Resolution, Nvidia Broadcast, cutting-edge AV1 encoding, class-leading ray tracing, Nvidia Reflex, and more are on tap, and they’re all truly excellent.

Brad Chacos/IDG
Brad Chacos/IDG
Brad Chacos/IDG
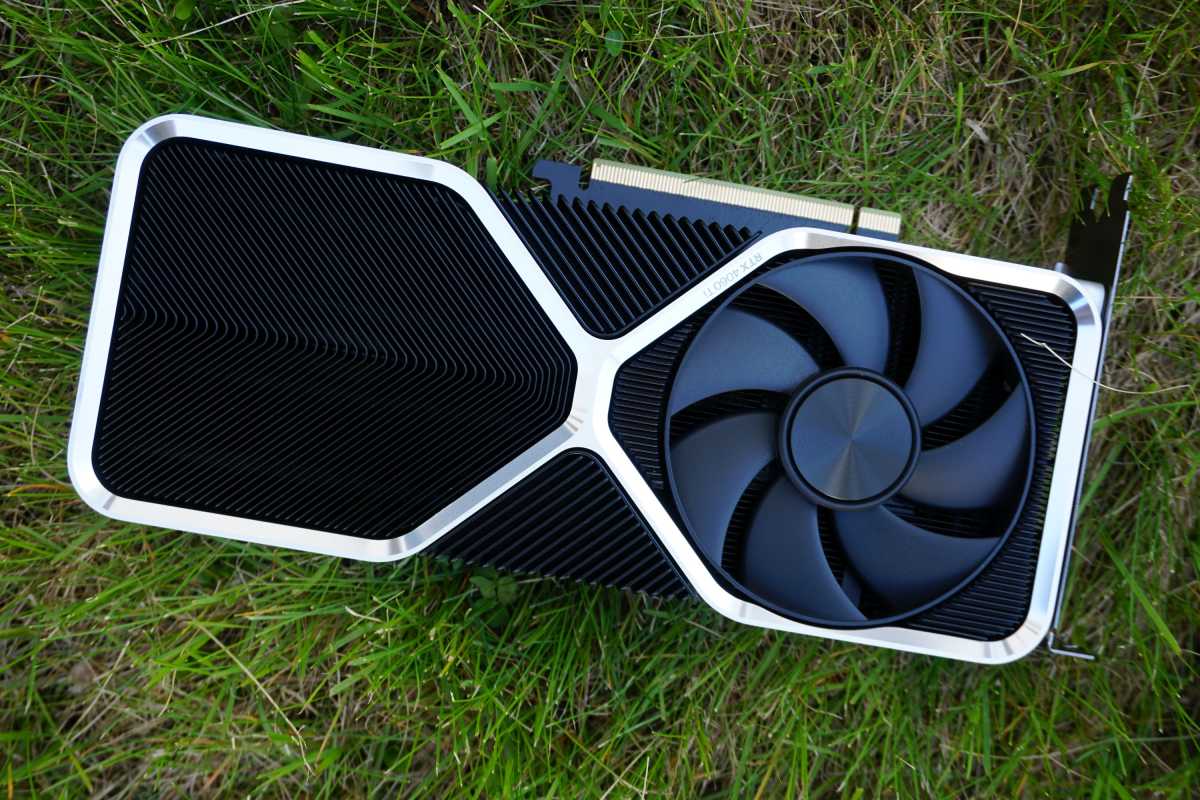
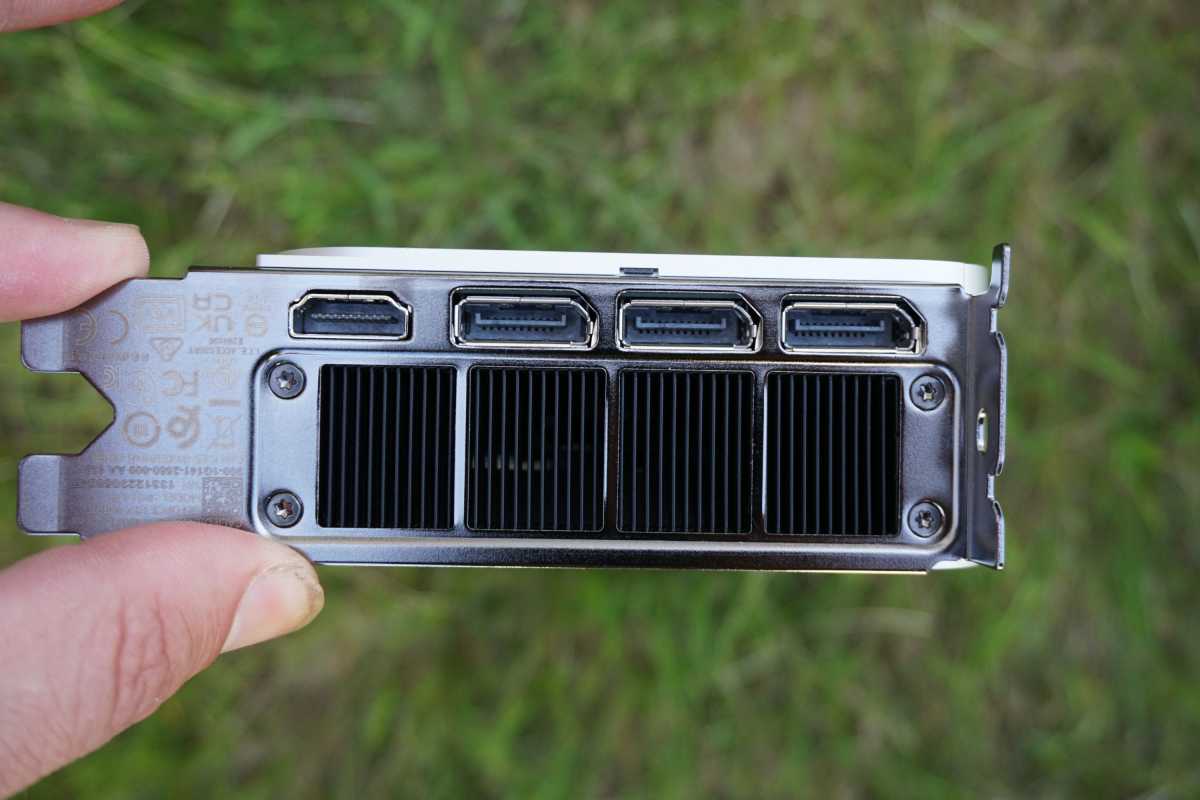
We’re testing Nvidia’s GeForce RTX 4060 Ti Founders Edition, a manageable two-slot iteration of the company’s tried-and-tried and gorgeous in-house design. It’s more silver than upper-tier models, coming with a single HDMI slot and three DisplayPorts.

Brad Chacos/IDG
Brad Chacos/IDG
Brad Chacos/IDG
One quibble: Despite only requiring a single 8-pin connector for power, Nvidia still outfit the card with a 12VHPWR cable, necessitating the use of a short adapter included in box. It looks awkward and fugly if you’re using a case with a windowed side. The fan blades are also much less densely packed than previous FE models, though it doesn’t affect cooling performance, as you’ll see later on.

Brad Chacos/IDG
Brad Chacos/IDG
Brad Chacos/IDG
Enough chatter. Let’s get to the games!
Our test system
We test graphics cards on an AMD Ryzen 5900X PC used exclusively for benchmarking GPUs. We now test with PCIe Resizable BAR (also known as Smart Access Memory on Ryzen systems) active, as most modern gaming PCs released in the last four years support the performance-boosting feature, either natively or via a motherboard firmware update. Nvidia also recommends turning on the optional “Hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling” in Windows to let the RTX 40-series stretch its legs to the fullest, so we’ve made that tweak as well. Most of the hardware was provided by the manufacturers, but we purchased the storage ourselves.
AMD Ryzen 5900X, stock settingsAMD Wraith Max coolerMSI Godlike X570 motherboard32GB G.Skill Trident Z Neo DDR4 3800 memory, XMP activeCorsair HX1500i power supply (and optional $20 12VHPWR 600 cable for Nvidia GPUs)1TB SK Hynix Gold S31 SSD x2
We test a variety of games spanning various engines, genres, vendor sponsorships (Nvidia, AMD, and Intel), and graphics APIs (DirectX 9, 11, DX12, and Vulkan), to try to represent a full range of performance potential. Each game is tested using its in-game benchmark, sanity checked by Nvidia’s FrameView tool, at the highest possible graphics presets unless otherwise noted, with VSync, frame rate caps, real-time ray tracing or DLSS effects, and FreeSync/G-Sync disabled, along with any other vendor-specific technologies like FidelityFX tools or Nvidia Reflex. We’ve also enabled temporal anti-aliasing (TAA) to push these cards to their limits.
We run each benchmark at least three times and list the average result for each test. Outside of esports, we’ve limited our benchmarks to 1440p and 1080p resolutions, as the 4060 Ti truly isn’t built for 4K gaming. We test features like ray tracing and DLSS in a separate section, as upscaling features like DLSS and AMD’s rival FSR tweak the look of games to help them run faster.
Usually we present our data in a series of per-game bar charts, but given some severe time constraints, we’re running our data in raw charts today and supplementing it with additional performance commentary instead. (Hit me up on Twitter to let me know if you love it or hate it!) Those time restrictions also prevented us from running new benchmark data for the $330 16GB Intel Arc A770, alas, which is another strong contender in this price segment.
Nvidia GeForce RTX 4060 Ti 1080p gaming performance
Nvidia itself calls the RTX 4060 Ti “a 1080p performance champ,” so let’s start there.
Right-click and open in new tab to see in full resolution.
Right-click and open in new tab to see in full resolution.
Brad Chacos/IDG
Right-click and open in new tab to see in full resolution.
Brad Chacos/IDG
Brad Chacos/IDG
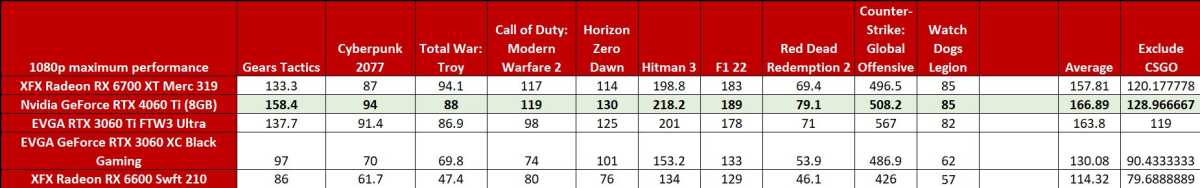
All of these graphics cards deliver great 1080p graphics performance with eye candy maxed out, even the last-gen Radeon RX 6600, which can be found hovering around $200 these days. We also included results for the Radeon RX 6700 XT. This AMD GPU features 12GB of VRAM and a 256-bit bus, sidestepping concerns with the RTX 4060 Ti’s memory configuration. It can be found for roughly $350 these days.
The new RTX 4060 Ti generally leads its RTX 3060 Ti predecessor, albeit by a slim to negligible margin in most games, as evidenced by the average FPS shown at the end of the chart.
The one exception? The legendary Counter-Strike: Global Offensive, one of the most-played games on the planet. GeForce RTX 40-series GPUs have consistently failed to beat their predecessors in CSGO, likely due to the much narrower memory bus widths that Nvidia slapped on this generation. If you exclude CSGO and its ultra-high frame rates from the averaged results, the RTX 4060 Ti’s lead widens, hitting 130fps on average versus the RTX 3060 Ti’s 119—still a paltry 9 percent uplift overall.
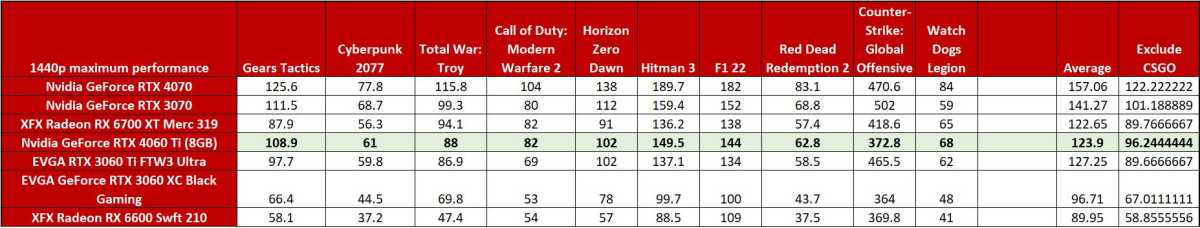
Nvidia GeForce RTX 4060 Ti 1440p gaming performance
We also tested these cards at 1440p resolution, adding in the $500 RTX 3070 from last generation and the new $599 RTX 4070 for good measure (literally).
Right-click and open in new tab to see in full resolution.
Right-click and open in new tab to see in full resolution.
Brad Chacos/IDG
Right-click and open in new tab to see in full resolution.
Brad Chacos/IDG
Brad Chacos/IDG
Once again, all these graphics cards turn in a respectable showing, and once again, the new RTX 4060 Ti lands uncomfortably close to its predecessor. Factoring in CSGO’s high frame rates and slower RTX 40-series performance, the 3060 Ti actually holds the lead in the averaged frame rate here. Oof. That’s a bit misleading though, because the RTX 3060 Ti is so much faster than the RTX 4060 Ti at 1440p that it skews the overall picture. Exclude CSGO and the RTX 4060 Ti is roughly 7 percent faster than the RTX 3060 Ti. Still oof.
That oof becomes an OOF when you consider the RTX 3070’s performance. It smashes the RTX 4060 Ti to the tune of a 13.7 percent average with CSGO included, or by 5 percent with CSGO excluded. Not being able to beat a card that cost just $100 more 2.5 years ago is deeply embarrassing for Nvidia’s new GPU, and an indication of why the RTX 4060 Ti’s new technical configuration makes it unsuitable for long-term 1440p gaming performance.
Speaking of, peep that Radeon RX 6700 XT at both resolutions. It performs similarly on average to the RTX 3060 Ti, which as we just established is within spitting distance of the RTX 4060 Ti, but comes with 12GB of memory and a wider 256-bit bus for $350. If you’re worried about 8GB not being enough VRAM for modern games, or want to dabble in 1440p gaming and don’t mind giving up DLSS and other Nvidia features, it’s worth considering—especially at $50 less than Nvidia’s new GPU. When it comes to VRAM capacity, either you have enough or you don’t.
DLSS 3 Frame Generation is a feather in the cap of the RTX 4060 Ti—just flip it on and watch the frame rate fly.
Nvidia GeForce RTX 4060 Ti ray tracing, DLSS, and DLSS 3 performance
So the RTX 4060 Ti is a mediocre generational upgrade when it comes to traditional gaming horsepower. Nvidia is seemingly hitching this GPU’s hat on power efficiency (more on that later), ray tracing, and—given the nature of the performance metrics Nvidia unveiled in the card’s announcement—the power of AI-enhanced DLSS performance improvements.
Fortunately, many of the games in our carefully chosen test suite include ray tracing and image upscaling (Nvidia DLSS/AMD FSR) options. We test the games at native, native with RT on Ultra, and with RT on Ultra and DLSS/FSR on Balanced to evaluate each experience.
BUT!
It’s worth noting that I think DLSS/FSR image upscaling looks terrible at the 1080p resolution this graphics card was built for. Image upscaling works by internally rendering a frame at a lower resolution, then using AI and/or software tricks to upscale the final image to match your chosen resolution. It lets you get faster performance with minimal to no loss in image quality—at least at higher pixel-packed 1440p and 4K resolutions.
Activating image upscaling isn’t so simple at 1080p. At this lower end of the scale, the image upscaling technology is pulling from so many fewer pixels that the visuals that appear onscreen can look blurry and jagged, even at higher-quality DLSS/FSR presets. The internal image being used to render games at 1080p resolution with DLSS Balanced on is under 720p—and it looks like it, in my opinion, though DLSS looks superior to AMD’s FSR at this resolution.
I wouldn’t buy a 1080p graphics card with upscaling in mind, full stop. Unfortunately, the lower upscaled image fidelity also makes running ray tracing more difficult at 1080p, as it takes away from the enhanced visuals that ray tracing can provide. The best lighting in the world doesn’t look great when it’s paired with jagged, blurry models, alas. It’s fine enough if need be, though.
Image upscaling is just part of the DLSS value proposition with the RTX 40-series however. This generation also marks the introduction of DLSS 3 Frame Generation, which leverages the tensor cores and enhanced optical flow accelerator within Nvidia’s Lovelace GPUs to insert fully AI-generated frames between every traditionally rendered frame.
This is a true potential feather in the cap of the RTX 4060 Ti. You don’t have to activate DLSS 2 image upsampling and downgrade image fidelity to run DLSS 3—you can just flip on Frame Generation and watch the frame rate fly, especially in CPU-bound games like Microsoft Flight Simulator. It’s fantastic.
That said, DLSS 3 isn’t quite set-and-forget either. Inserting AI frames can sometimes result in visual artifacts in select games, especially around UI elements. And since you can’t actually control inputs during those AI-generated frames, latency is added. DLSS 3 requires developers to also integrate Nvidia Reflex to combat those concerns, which often helps games be slightly more responsive than when rendering natively, but it doesn’t result in the jump in responsiveness you’d normally expect when supercharging your frame rates. That means the feel of the game might not match what your brain and hands expect—a game might be running 50 percent-plus faster with frame generation on, for example, but only feel 10 to 20 percent faster in responsiveness.
DLSS 3 makes games look amazing to be sure, but that detail is kind of weird, and worth noting. Our DLSS 3 deep dive goes into everything about the technology in much greater detail.
Right-click and open in new tab to see in full resolution.
Note that Watch Dogs doesn’t support FSR, hence the 0 FPS on AMD GPUs there.
Right-click and open in new tab to see in full resolution.
Note that Watch Dogs doesn’t support FSR, hence the 0 FPS on AMD GPUs there.
Brad Chacos/IDG
Right-click and open in new tab to see in full resolution.
Note that Watch Dogs doesn’t support FSR, hence the 0 FPS on AMD GPUs there.
Brad Chacos/IDG
Brad Chacos/IDG
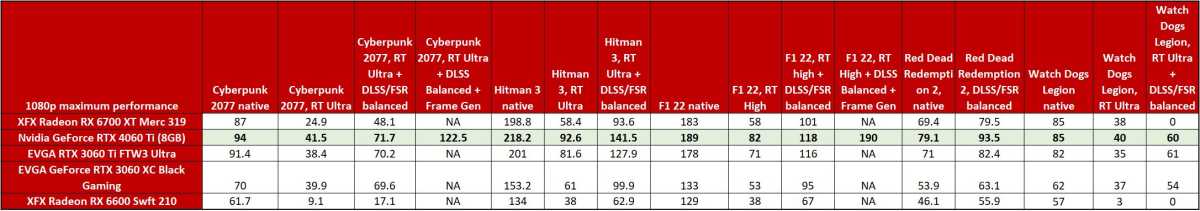
We tested ray tracing and DLSS at both 1440p and 1080p resolution, but are only revealing the 1080p results above, given a combination of time constraints and the fact that you should only really consider the RTX 4060 Ti for 1080p gaming.
As you can see from these numbers, the RTX 4060 Ti maintains Nvidia’s ray tracing lead in this segment, though it doesn’t functionally extend it beyond what the 3060 Ti was already capable of years ago for the same price. We test at Ultra, but if you dial some graphics settings back to High or Medium, you can come close to 60fps performance at 1080p in many games even with ray tracing enabled and DLSS off. DLSS 3 is a game changer when it’s available, but note that it’s only currently available in about 50 titles.
How are the RTX 4060 Ti’s power efficiency and thermals?
Excellent.
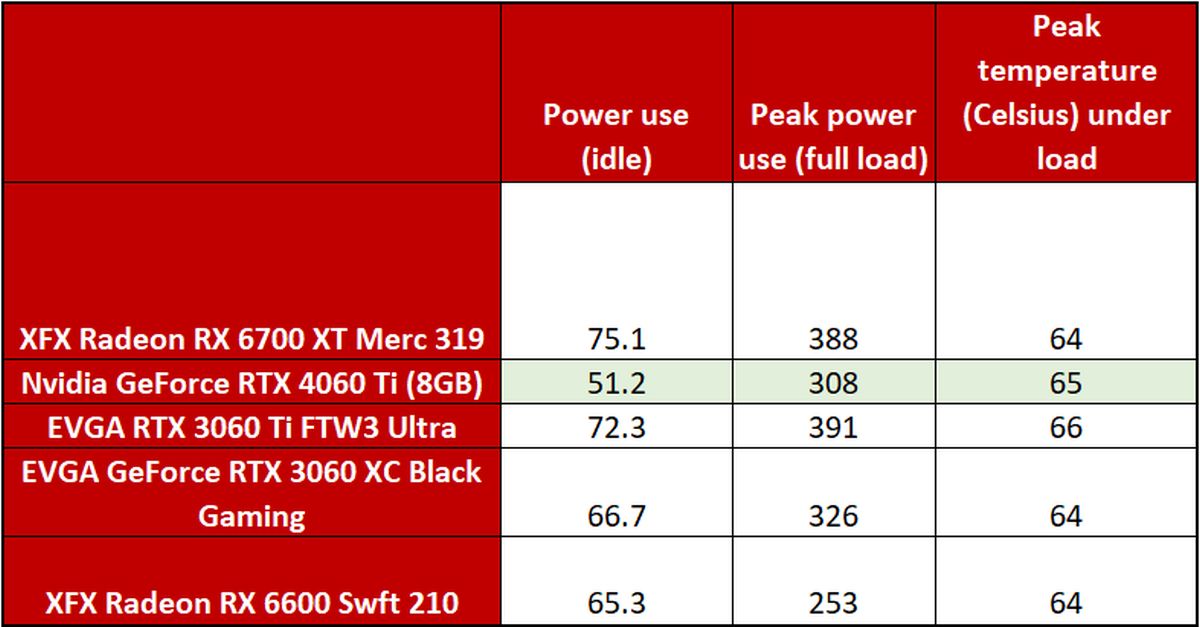
We test power draw by looping the F1 22 benchmark at 4K for about 20 minutes after we’ve benchmarked everything else (to warm up the GPU) and noting the highest reading on our Watts Up Pro meter, which measures the power consumption of our entire test system. The initial part of the race, where all competing cars are onscreen simultaneously, tends to be the most demanding portion. This isn’t a worst-case test; this is a GPU-bound game running at a GPU-bound resolution to gauge performance when the graphics card is sweating hard. If you’re playing a game that also hammers the CPU, you could see higher overall system power draws. Consider yourself warned.
The GeForce RTX 4060 Ti absolutely sips power despite flinging out fast frame rates, drawing 83 fewer watts than the RTX 3060 Ti despite being 7 to 9 percent faster in performance. And that idle power is absolutely bonkers.
Brad Chacos/IDG
Brad Chacos/IDG
Brad Chacos/IDG
We test thermals by leaving GPU-Z open during the F1 22 power draw test, noting the highest maximum temperature at the end.
No surprise here. The tiny two-slot Founders Edition design does a fine job keeping this ultra-efficient GPU running cold. Custom 4060 Ti models with mammoth coolers might run quieter—the FE delivers fine noise levels, albeit not silent—but there’s no need to improve on temperatures alone.
Should you buy the GeForce RTX 4060 Ti?
It all depends on your answer to the question posed right up top: Are you willing to pay $400 for a 1080p graphics card with 8GB of memory in the year of our lord 2023?
The GeForce RTX 4060 Ti delivers absolutely outstanding power efficiency, leading ray tracing performance, modern AV1 encoding, and fast 1080p gaming for high refresh rate monitors, backed by Nvidia’s knockout software suite: DLSS 3 Frame Generation, Nvidia Reflex, RTX Video Super Resolution, and Nvidia Broadcast are just some of the killer features available to the RTX 4060 Ti, with DLSS 3 only being available on Nvidia’s newest GPU in this price segment. If you’re still on a GTX 1060 or RTX 2060, the RTX 4060 Ti will be a fantastic upgrade (albeit expensive).
It’ll be a hard sell for many folks, though—just like the RTX 4080, 4070 Ti, and 4070 have been so far this seemingly lost generation.

Brad Chacos/IDG
Brad Chacos/IDG
Brad Chacos/IDG
Nvidia pitches the GeForce RTX 4060 Ti as “a 1080p performance champ,” and if you’ve followed along with our technical dissection and benchmarks, that’s exactly what it is. Memory and GPU configuration decisions made by Nvidia keep this GPU from flexing its muscles at 1440p (though you can certainly game at 1440p if you don’t mind tweaking graphics settings). That’s exacerbated by its 8GB of onboard memory.
As Hardware Unboxed recently chronicled, 8GB of memory isn’t enough to run all modern games maxed-out now that developers are taking advantage of the 16GB shared memory pools in the Xbox Series X and PlayStation 5. In Nvidia’s own early RTX 4060 Ti performance teasers, it had to reduce graphics settings in A Plague Tale: Requiem and Resident Evil Remake even at 1080p, while recent games like The Last of Us and Hogwarts Legacy also struggle with 8GB at the lower resolution unless you drop settings.
Frame Generation is pretty damned cool, but Nvidia’s vaunted DLSS upsampling loses quite a bit of its luster at 1080p (along with AMD’s rival FSR) because of the limited amount of pixels available at this resolution. I wouldn’t run 1080p games with DLSS or FSR active aside from the specific DLSS 3 Frame Generation feature. Even then, while DLSS 3 is off to a hot start, it’s only currently available in around 50 games.
The RTX 4060 Ti is also a deeply uninspiring upgrade gen-on-gen when it comes to raw GPU horsepower, only besting the RTX 3060 Ti by 9 percent at 1080p resolution and 7 percent at 1440p. It has fewer CUDA, RT, and tensor cores than its predecessor, which is disappointing. It flat-out loses to the RTX 3070 at 1440p, which is even more disappointing.
So: Are you willing to pay $400 for a 1080p graphics card with 8GB of memory in the year of our lord 2023? I’m not, especially with DLSS/FSR advantages minimized in this segment. (Given the RTX 4060 Ti’s overall performance, I don’t think the $500 16GB version will be very appealing when it launches in July either.)
Our favorite affordable 1080p gpu for 60Hz gaming
Radeon RX 6600 Swft 210
 Read our reviewPrice When Reviewed:$329.99Best Prices Today:$199.99 at Amazon | $229.99 at Newegg
Read our reviewPrice When Reviewed:$329.99Best Prices Today:$199.99 at Amazon | $229.99 at Newegg
If you have to buy right now, I’d rather spend my money on a Radeon RX 6600 for around $200 if I was gaming on a 1080p/60Hz monitor, or opt for the Radeon RX 6700 XT and its 12GB of memory on a 256-bit bus for $350 if you’re thinking about dabbling in 1440p, worried about 8GB of VRAM being enough at 1080p, and don’t mind giving up DLSS 3. (Intel’s $330 Arc A770 offers 16GB of VRAM, on that note.) Since the RTX 4060 Ti doesn’t provide a tangible performance upgrade over the RTX 3060 Ti and is slower than the RTX 3070, you might also be able to snap up either of those on sale to take advantage of Nvidia’s awesome features, though note that those both lack DLSS 3 support and are also limited to 8GB of memory, so look for steep sales.
That said, I’d hold my horses if I could. Nvidia already teased a $299 RTX 4060 with DLSS 3, AV1, and extreme power efficiency for July. Plus, the rumor mill is screaming that AMD could launch a $300 Radeon RX 7600 any minute now. That price point is a lot more palatable for 1080p gaming on 8GB if you don’t need Nvidia’s deep feature set.
The GeForce RTX 4060 Ti would have been more appealing if it offered 16GB of memory for $399 and ditched the 8GB option, or offered 8GB of memory with the same level of performance for $300 to $325. As it stands, Nvidia’s RTX 40-series upgrades remain uninspiring at best and this GPU sadly falls into a no-man’s land of sorts. Look elsewhere.
Best Prices Today: GeForce RTX 4060 Ti (8GB)
RetailerPrice $399View DealPrice comparison from over 24,000 stores worldwideProductPricePrice comparison from Backmarket
$399View DealPrice comparison from over 24,000 stores worldwideProductPricePrice comparison from Backmarket
Author: Brad Chacos, Executive editor

Brad Chacos spends his days digging through desktop PCs and tweeting too much. He specializes in graphics cards and gaming, but covers everything from security to Windows tips and all manner of PC hardware.
Recent stories by Brad Chacos:
Nvidia GeForce RTX 4080 Super review: The 4K graphics card you wantNew Arc drivers provide huge DX11 performance boost for Intel GPUsSteam gamers love Nvidia’s GeForce RTX 3060. Is it still worth buying in 2024?





