New geospatial data startup streamlines satellite imagery visualization

These days we have a ton of geospatial data coming off the increasing numbers of satellites circling in our atmosphere, but it takes some serious processing power and engineering prowess to turn that data into something useful.
A couple of former Uber engineers, Sina Kashuk and Isaac Brodsky, who helped build the mapping system at Uber, decided to put their knowledge to work on the problem, and what they’ve come up with is a fast, serverless-based product that takes advantage of some open source tooling they’ve built to get that data from the source and into apps where it can be put to work.
Today, the startup emerged from stealth with the Fused platform, and $1 million in pre-seed funding.
Fused is a three-part system. It takes data, fed from satellites, sitting in storage repositories and runs it through its platform to make it usable. The end goal is to create visual representations of things like weather, deforestation or crop data and put the data to work in applications that people use like Excel, Airtable or Notion. The thing that separates it from what came before it is simplicity and processing speed.
Kashuk, who is co-founder and CEO at Fused, says the company took some time to create the current solution. In fact, after leaving Uber, they formed another company in 2019 called Unfolded.ai that was looking at a similar data visualization problem, but was acquired very quickly by Foursquare.
“The main challenge that we had with Unfolded was it was very hard to get to market because the majority of the platform was open source and people were like, ‘why do I have to pay you guys, when I can just use the open source’,” Kashuk told TechCrunch.
That was a business model problem, but they also ran into limitations because they were trying to run a front-end solution locally on a laptop, and as the data scaled it got very slow. As they were thinking about their next business, Kashuk and Brodsky saw this opportunity with data coming off of the growing number of commercial satellites, and they realized that the data processing on the back end remained a challenge, and could be a business.
Specifically, the founders saw the maturation of serverless computing, where the vendor can handle all of the back-end infrastructure, as an opportunity to help customers process this data and put it to use faster and more efficiently. “So the movement of serverless combined with massive amounts of data coming off of the growing commercial satellite industry made us believe that the industry was ready for this kind of shift,” Kashuk said.
The platform is essentially a middleware processing layer that helps turn the geospatial data into something more consumable. It consists of several open source pieces and a serverless processing engine. It is the latter where the company makes money. Each time data hits the API gateway to the serverless back end, Fused gets paid.
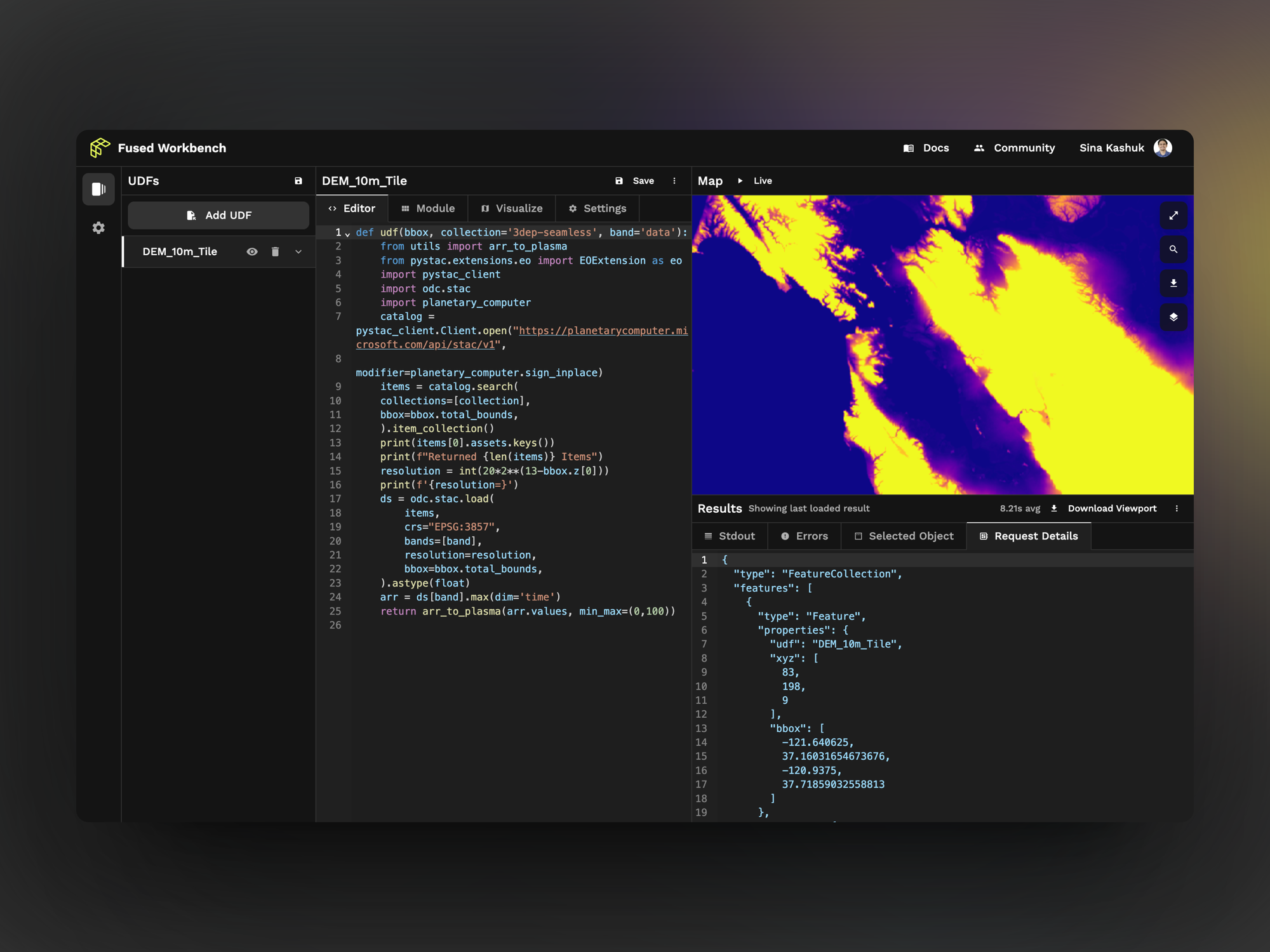
The entire system is built with Python, which is widely used by data scientists and developers. The system starts with a kind of visualization template called a user-defined function or UDF. This part is open source, enabling the community to create these templates, such as crop yields, and then using other pieces of the Fused platform, they can begin to break down the data such as the amount of wheat produced by U.S. state or any geographical area you wish.
They can then transfer this data to other programs for further analysis or create data visualizations based on the data. One of the big differentiators here is the speed at which Fused creates these visualizations or processes changes to them. Instead of taking hours, it takes seconds, according to the company.
One of the key platform pieces involved in creating the visualizations is the Fused Workbench, which is available starting today. The Workbench, while partially open, only works in conjunction with the back-end API, he says, but lets you interact with the data to see different aspects and see your changes almost instantly.
The company launched last year and has been working with early beta customers before emerging today. The $1 million in pre-seed came from Fontinalis Partners along with various industry angels.



